Java interview questions
Java Interview Questions
Table of Contents
In this Java Interview Questions blog, I am going to list some of the most important Java Interview Questions and Answers which will set you apart in the interview process. Java is used by approx 10 Million developers worldwide to develop applications for 15 Billion devices supporting Java. It is also used to create applications for trending technologies like Big Data to household devices like Mobiles and DTH boxes. And hence today, Java is used everywhere! This is the reason why Java Certification is the most in-demand certification in the programming domain.
Basic Java Interview Questions
Q1. Explain JDK, JRE and JVM?
| JDK | JRE | JVM |
| It stands for Java Development Kit. | It stands for Java Runtime Environment. | It stands for Java Virtual Machine. |
| It is the tool necessary to compile, document and package Java programs. | JRE refers to a runtime environment in which Java bytecode can be executed. | It is an abstract machine. It is a specification that provides a run-time environment in which Java bytecode can be executed. |
| It contains JRE + development tools. | It’s an implementation of the JVM which physically exists. | JVM follows three notations: Specification, Implementation, and Runtime Instance. |
Q2. Explain public static void main(String args[]) in Java.
main() in Java is the entry point for any Java program. It is always written as public static void main(String[] args).
- public: Public is an access modifier, which is used to specify who can access this method. Public means that this Method will be accessible by any Class.
- static: It is a keyword in java which identifies it is class-based. main() is made static in Java so that it can be accessed without creating the instance of a Class. In case, main is not made static then the compiler will throw an error as main() is called by the JVM before any objects are made and only static methods can be directly invoked via the class.
- void: It is the return type of the method. Void defines the method which will not return any value.
- main: It is the name of the method which is searched by JVM as a starting point for an application with a particular signature only. It is the method where the main execution occurs.
- String args[]: It is the parameter passed to the main method.
Q3. Why Java is platform independent?
Java is called platform independent because of its byte codes which can run on any system irrespective of its underlying operating system.
Q4. Why Java is not 100% Object-oriented?
Java is not 100% Object-oriented because it makes use of eight primitive data types such as boolean, byte, char, int, float, double, long, short which are not objects.
Q5. What are wrapper classes in Java?
Wrapper classes convert the Java primitives into the reference types (objects). Every primitive data type has a class dedicated to it. These are known as wrapper classes because they “wrap” the primitive data type into an object of that class. Refer to the below image which displays different primitive type, wrapper class and constructor argument.
Q6. What are constructors in Java?
In Java, constructor refers to a block of code which is used to initialize an object. It must have the same name as that of the class. Also, it has no return type and it is automatically called when an object is created.
There are two types of constructors:
- Default Constructor: In Java, a default constructor is the one which does not take any inputs. In other words, default constructors are the no argument constructors which will be created by default in case you no other constructor is defined by the user. Its main purpose is to initialize the instance variables with the default values. Also, it is majorly used for object creation.
- Parameterized Constructor: The parameterized constructor in Java, is the constructor which is capable of initializing the instance variables with the provided values. In other words, the constructors which take the arguments are called parameterized constructors.
Q7. What is singleton class in Java and how can we make a class singleton?
Singleton class is a class whose only one instance can be created at any given time, in one JVM. A class can be made singleton by making its constructor private.
Q8. What is the difference between Array list and vector in Java?
| ArrayList | Vector |
|---|---|
| Array List is not synchronized. | Vector is synchronized. |
| Array List is fast as it’s non-synchronized. | Vector is slow as it is thread safe. |
| If an element is inserted into the Array List, it increases its Array size by 50%. | Vector defaults to doubling size of its array. |
| Array List does not define the increment size. | Vector defines the increment size. |
| Array List can only use Iterator for traversing an Array List. | Vector can use both Enumeration and Iterator for traversing. |
Q9. What is the difference between equals() and == in Java?
Equals() method is defined in Object class in Java and used for checking equality of two objects defined by business logic.
“==” or equality operator in Java is a binary operator provided by Java programming language and used to compare primitives and objects. public boolean equals(Object o) is the method provided by the Object class. The default implementation uses == operator to compare two objects. For example: method can be overridden like String class. equals() method is used to compare the values of two objects.
Q10. What are the differences between Heap and Stack Memory in Java?
The major difference between Heap and Stack memory are:
| Features | Stack | Heap |
|---|---|---|
| Memory | Stack memory is used only by one thread of execution. | Heap memory is used by all the parts of the application. |
| Access | Stack memory can’t be accessed by other threads. | Objects stored in the heap are globally accessible. |
| Memory Management | Follows LIFO manner to free memory. | Memory management is based on the generation associated with each object. |
| Lifetime | Exists until the end of execution of the thread. | Heap memory lives from the start till the end of application execution. |
| Usage | Stack memory only contains local primitive and reference variables to objects in heap space. | Whenever an object is created, it’s always stored in the Heap space. |
Q11. What is a package in Java? List down various advantages of packages.
Packages in Java, are the collection of related classes and interfaces which are bundled together. By using packages, developers can easily modularize the code and optimize its reuse. Also, the code within the packages can be imported by other classes and reused. Below I have listed down a few of its advantages:
- Packages help in avoiding name clashes
- They provide easier access control on the code
- Packages can also contain hidden classes which are not visible to the outer classes and only used within the package
- Creates a proper hierarchical structure which makes it easier to locate the related classes
Q12. Why pointers are not used in Java?
Java doesn’t use pointers because they are unsafe and increases the complexity of the program. Since, Java is known for its simplicity of code, adding the concept of pointers will be contradicting. Moreover, since JVM is responsible for implicit memory allocation, thus in order to avoid direct access to memory by the user, pointers are discouraged in Java.
Q13. What is JIT compiler in Java?
JIT stands for Just-In-Time compiler in Java. It is a program that helps in converting the Java bytecode into instructions that are sent directly to the processor. By default, the JIT compiler is enabled in Java and is activated whenever a Java method is invoked. The JIT compiler then compiles the bytecode of the invoked method into native machine code, compiling it “just in time” to execute. Once the method has been compiled, the JVM summons the compiled code of that method directly rather than interpreting it. This is why it is often responsible for the performance optimization of Java applications at the run time.
Q14. What are access modifiers in Java?
In Java, access modifiers are special keywords which are used to restrict the access of a class, constructor, data member and method in another class. Java supports four types of access modifiers:
- Default
- Private
- Protected
- Public
| Modifier | Default | Private | Protected | Public |
| Same class | YES | YES | YES | YES |
| Same Package subclass | YES | NO | YES | YES |
| Same Package non-subclass | YES | NO | YES | YES |
| Different package subclass | NO | NO | YES | YES |
| Different package non-subclass | NO | NO | NO | YES |
Q15. Define a Java Class.
A class in Java is a blueprint which includes all your data. A class contains fields (variables) and methods to describe the behavior of an object. Let’s have a look at the syntax of a class.
|
1
2
3
|
class Abc {member variables // class bodymethods} |
Q16. What is an object in Java and how is it created?
An object is a real-world entity that has a state and behavior. An object has three characteristics:
- State
- Behavior
- Identity
An object is created using the ‘new’ keyword. For example:
ClassName obj = new ClassName();
Q17. What is Object Oriented Programming?
Object-oriented programming or popularly known as OOPs is a programming model or approach where the programs are organized around objects rather than logic and functions. In other words, OOP mainly focuses on the objects that are required to be manipulated instead of logic. This approach is ideal for the programs large and complex codes and needs to be actively updated or maintained.
Q18. What are the main concepts of OOPs in Java?
Object-Oriented Programming or OOPs is a programming style that is associated with concepts like:
- Inheritance: Inheritance is a process where one class acquires the properties of another.
- Encapsulation: Encapsulation in Java is a mechanism of wrapping up the data and code together as a single unit.
- Abstraction: Abstraction is the methodology of hiding the implementation details from the user and only providing the functionality to the users.
- Polymorphism: Polymorphism is the ability of a variable, function or object to take multiple forms.
Q19. What is the difference between a local variable and an instance variable?
In Java, a local variable is typically used inside a method, constructor, or a block and has only local scope. Thus, this variable can be used only within the scope of a block. The best benefit of having a local variable is that other methods in the class won’t be even aware of that variable.
Example
|
1
2
3
4
|
if(x > 100){String test = "codeplayon";} |
Whereas, an instance variable in Java, is a variable which is bounded to its object itself. These variables are declared within a class, but outside a method. Every object of that class will create it’s own copy of the variable while using it. Thus, any changes made to the variable won’t reflect in any other instances of that class and will be bound to that particular instance only.
|
1
2
3
4
|
class Test{public String EmpName;public int empAge;} |
Q20. Differentiate between the constructors and methods in Java?
| Methods | Constructors |
| 1. Used to represent the behavior of an object | 1. Used to initialize the state of an object |
| 2. Must have a return type | 2. Do not have any return type |
| 3. Needs to be invoked explicitly | 3. Is invoked implicitly |
| 4. No default method is provided by the compiler | 4. A default constructor is provided by the compiler if the class has none |
| 5. Method name may or may not be same as class name | 5. Constructor name must always be the same as the class name |
Q21. What is final keyword in Java?
final is a special keyword in Java that is used as a non-access modifier. A final variable can be used in different contexts such as:
- final variable
When the final keyword is used with a variable then its value can’t be changed once assigned. In case the no value has been assigned to the final variable then using only the class constructor a value can be assigned to it.
-
final method
When a method is declared final then it can’t be overridden by the inheriting class.
-
final class
When a class is declared as final in Java, it can’t be extended by any subclass class but it can extend other class.
Q22. What is the difference between break and continue statements?
| break | continue |
| 1. Can be used in switch and loop (for, while, do while) statements | 1. Can be only used with loop statements |
| 2. It causes the switch or loop statements to terminate the moment it is executed | 2. It doesn’t terminate the loop but causes the loop to jump to the next iteration |
| 3. It terminates the innermost enclosing loop or switch immediately | 3. A continue within a loop nested with a switch will cause the next loop iteration to execute |
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
|
for (int i = 0; i < 5; i++){if (i == 3){break;}System.out.println(i);} |
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
|
for (int i = 0; i < 5; i++){if(i == 2){continue;}System.out.println(i);} |
Q23.What is an infinite loop in Java? Explain with an example.
An infinite loop is an instruction sequence in Java that loops endlessly when a functional exit isn’t met. This type of loop can be the result of a programming error or may also be a deliberate action based on the application behavior. An infinite loop will terminate automatically once the application exits.
For example:
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
|
public class InfiniteForLoopDemo{public static void main(String[] arg) {for(;;)System.out.println("Welcome to codeplayon!");// To terminate this program press ctrl + c in the console.}} |
Q24. What is the difference between this() and super() in Java?
In Java, super() and this(), both are special keywords that are used to call the constructor.
| this() | super() |
| 1. this() represents the current instance of a class | 1. super() represents the current instance of a parent/base class |
| 2. Used to call the default constructor of the same class | 2. Used to call the default constructor of the parent/base class |
| 3. Used to access methods of the current class | 3. Used to access methods of the base class |
| 4. Used for pointing the current class instance | 4. Used for pointing the superclass instance |
| 5. Must be the first line of a block | 5. Must be the first line of a block |
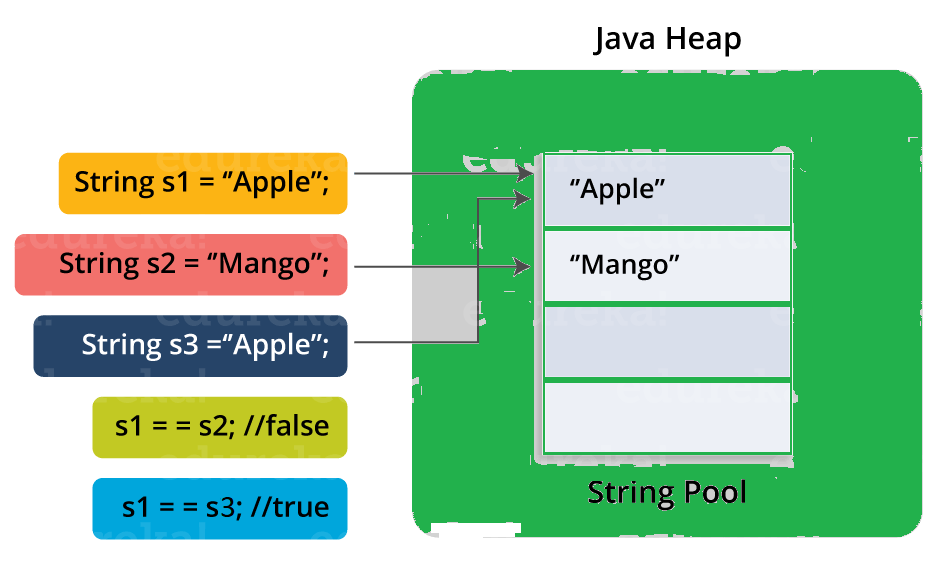
Q25. What is Java String Pool?
Java String pool refers to a collection of Strings which are stored in heap memory. In this, whenever a new object is created, String pool first checks whether the object is already present in the pool or not. If it is present, then the same reference is returned to the variable else new object will be created in the String pool and the respective reference will be returned.
Q26. Differentiate between static and non-static methods in Java.
| Static Method | Non-Static Method |
| 1. The static keyword must be used before the method name | 1. No need to use the static keyword before the method name |
| 2. It is called using the class (className.methodName) | 2. It is can be called like any general method |
| 3. They can’t access any non-static instance variables or methods | 3. It can access any static method and any static variable without creating an instance of the class |
Q27. What is constructor chaining in Java?
In Java, constructor chaining is the process of calling one constructor from another with respect to the current object. Constructor chaining is possible only through legacy where a subclass constructor is responsible for invoking the superclass’ constructor first. There could be any number of classes in the constructor chain. Constructor chaining can be achieved in two ways:
- Within the same class using this()
- From base class using super()
Q28. Difference between String, StringBuilder, and StringBuffer.
| Factor | String | StringBuilder | StringBuffer |
| Storage Area | Constant String Pool | Heap Area | Heap Area |
| Mutability | Immutable | Mutable | Mutable |
| Thread Safety | Yes | No | Yes |
| Performance | Fast | More efficient | Less efficient |
Q29. What is a classloader in Java?
The Java ClassLoader is a subset of JVM (Java Virtual Machine) that is responsible for loading the class files. Whenever a Java program is executed it is first loaded by the classloader. Java provides three built-in classloaders:
- Bootstrap ClassLoader
- Extension ClassLoader
- System/Application ClassLoader
Q30. Why Java Strings are immutable in nature?
In Java, string objects are immutable in nature which simply means once the String object is created its state cannot be modified. Whenever you try to update the value of that object instead of updating the values of that particular object, Java creates a new string object. Java String objects are immutable as String objects are generally cached in the String pool. Since String literals are usually shared between multiple clients, action from one client might affect the rest. It enhances security, caching, synchronization, and performance of the application.
Q31. What is the difference between an array and an array list?
| Array | ArrayList |
|---|---|
| Cannot contain values of different data types | Can contain values of different data types. |
| Size must be defined at the time of declaration | Size can be dynamically changed |
| Need to specify the index in order to add data | No need to specify the index |
| Arrays are not type parameterized | Arraylists are type |
| Arrays can contain primitive data types as well as objects | Arraylists can contain only objects, no primitive data types are allowed |
Q32. What is a Map in Java?
In Java, Map is an interface of Util package which maps unique keys to values. The Map interface is not a subset of the main Collection interface and thus it behaves little different from the other collection types. Below are a few of the characteristics of Map interface:
- Map doesn’t contain duplicate keys.
- Each key can map at max one value.
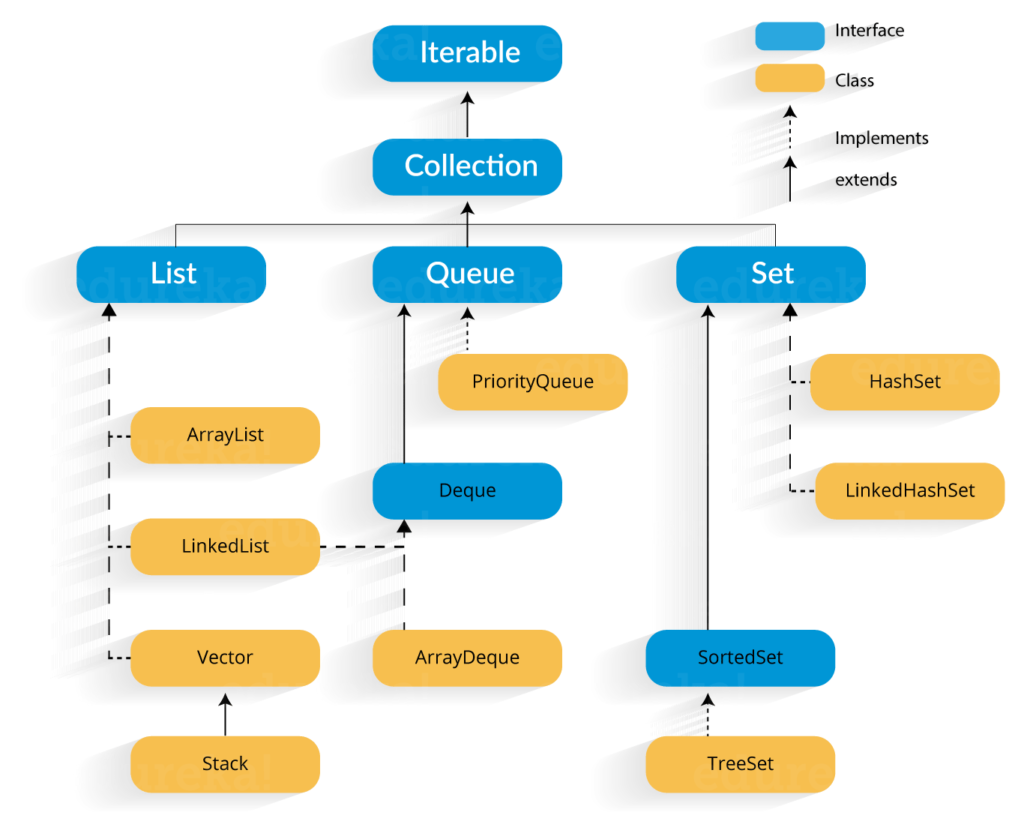
Q33. What is collection class in Java? List down its methods and interfaces.
In Java, the collection is a framework that acts as an architecture for storing and manipulating a group of objects. Using Collections you can perform various tasks like searching, sorting, insertion, manipulation, deletion, etc. Java collection framework includes the following:
- Interfaces
- Classes
- Methods
The below image shows the complete hierarchy of the Java Collection.
In case you are facing any challenges with these java interview questions, please comment on your problems in the section below.
OOPS Java Interview Questions
Q1. What is Polymorphism?
Polymorphism is briefly described as “one interface, many implementations”. Polymorphism is a characteristic of being able to assign a different meaning or usage to something in different contexts – specifically, to allow an entity such as a variable, a function, or an object to have more than one form. There are two types of polymorphism:
- Compile time polymorphism
- Run time polymorphism
Compile time polymorphism is method overloading whereas Runtime time polymorphism is done using inheritance and interface.
Q2. What is runtime polymorphism or dynamic method dispatch?
In Java, runtime polymorphism or dynamic method dispatch is a process in which a call to an overridden method is resolved at runtime rather than at compile-time. In this process, an overridden method is called through the reference variable of a superclass. Let’s take a look at the example below to understand it better.
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
|
class Car {void run(){System.out.println(“car is running”); }}class Audi extends Car {void run(){System.out.prinltn(“Audi is running safely with 100km”);}public static void main(String args[]){Car b= new Audi(); //upcastingb.run();}} |
Q3. What is abstraction in Java?
Abstraction refers to the quality of dealing with ideas rather than events. It basically deals with hiding the details and showing the essential things to the user. Thus you can say that abstraction in Java is the process of hiding the implementation details from the user and revealing only the functionality to them. Abstraction can be achieved in two ways:
- Abstract Classes (0-100% of abstraction can be achieved)
- Interfaces (100% of abstraction can be achieved)
Q4. What do you mean by an interface in Java?
An interface in Java is a blueprint of a class or you can say it is a collection of abstract methods and static constants. In an interface, each method is public and abstract but it does not contain any constructor. Thus, interface basically is a group of related methods with empty bodies. Example:
Q5. What is the difference between abstract classes and interfaces?
| Abstract Class | Interfaces |
|---|---|
| An abstract class can provide complete, default code and/or just the details that have to be overridden | An interface cannot provide any code at all, just the signature |
| In the case of an abstract class, a class may extend only one abstract class | A Class may implement several interfaces |
| An abstract class can have non-abstract methods | All methods of an Interface are abstract |
| An abstract class can have instance variables | An Interface cannot have instance variables |
| An abstract class can have any visibility: public, private, protected | An Interface visibility must be public (or) none |
| If we add a new method to an abstract class then we have the option of providing default implementation and therefore all the existing code might work properly | If we add a new method to an Interface then we have to track down all the implementations of the interface and define implementation for the new method |
| An abstract class can contain constructors | An Interface cannot contain constructors |
| Abstract classes are fast | Interfaces are slow as it requires extra indirection to find the corresponding method in the actual class |
Q6. What is inheritance in Java?
Inheritance in Java is the concept where the properties of one class can be inherited by the other. It helps to reuse the code and establish a relationship between different classes. Inheritance is performed between two types of classes:
- Parent class (Super or Base class)
- Child class (Subclass or Derived class)
A class which inherits the properties is known as Child Class whereas a class whose properties are inherited is known as Parent class.
Q7. What are the different types of inheritance in Java?
Java supports four types of inheritance which are:
- Single Inheritance: In single inheritance, one class inherits the properties of another i.e there will be only one parent as well as one child class.
- Multilevel Inheritance: When a class is derived from a class which is also derived from another class, i.e. a class having more than one parent class but at different levels, such type of inheritance is called Multilevel Inheritance.
- Hierarchical Inheritance: When a class has more than one child classes (subclasses) or in other words, more than one child classes have the same parent class, then such kind of inheritance is known as hierarchical.
- Hybrid Inheritance: Hybrid inheritance is a combination of two or more types of inheritance.
Q8. What is method overloading and method overriding?
Method Overloading :
- In Method Overloading, Methods of the same class shares the same name but each method must have a different number of parameters or parameters having different types and order.
- Method Overloading is to “add” or “extend” more to the method’s behavior.
- It is a compile-time polymorphism.
- The methods must have a different signature.
- It may or may not need inheritance in Method Overloading.
Let’s take a look at the example below to understand it better.
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
|
class Adder {Static int add(int a, int b){return a+b;}Static double add( double a, double b){return a+b;}public static void main(String args[]){System.out.println(Adder.add(11,11));System.out.println(Adder.add(12.3,12.6));}} |
Method Overriding:
- In Method Overriding, the subclass has the same method with the same name and exactly the same number and type of parameters and same return type as a superclass.
- Method Overriding is to “Change” existing behavior of the method.
- It is a run time polymorphism.
- The methods must have the same signature.
- It always requires inheritance in Method Overriding.
Let’s take a look at the example below to understand it better.
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
|
class Car {void run(){System.out.println(“car is running”); }Class Audi extends Car{void run(){System.out.prinltn("Audi is running safely with 100km");}public static void main( String args[]){Car b=new Audi();b.run();}} |
Q9. Can you override a private or static method in Java?
You cannot override a private or static method in Java. If you create a similar method with the same return type and same method arguments in child class then it will hide the superclass method; this is known as method hiding. Similarly, you cannot override a private method in subclass because it’s not accessible there. What you can do is create another private method with the same name in the child class. Let’s take a look at the example below to understand it better.
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
|
class Base {private static void display() {System.out.println("Static or class method from Base");}public void print() {System.out.println("Non-static or instance method from Base");}class Derived extends Base {private static void display() {System.out.println("Static or class method from Derived");}public void print() {System.out.println("Non-static or instance method from Derived");}public class test {public static void main(String args[]){Base obj= new Derived();obj1.display();obj1.print();}} |
Q10. What is multiple inheritance? Is it supported by Java?
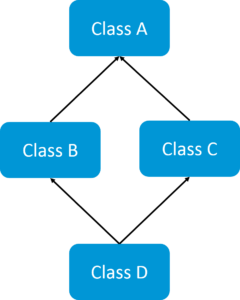 If a child class inherits the property from multiple classes is known as multiple inheritance. Java does not allow to extend multiple classes.
If a child class inherits the property from multiple classes is known as multiple inheritance. Java does not allow to extend multiple classes.
The problem with multiple inheritance is that if multiple parent classes have the same method name, then at runtime it becomes difficult for the compiler to decide which method to execute from the child class.
Therefore, Java doesn’t support multiple inheritance. The problem is commonly referred to as Diamond Problem.
Q11. What is encapsulation in Java?
Encapsulation is a mechanism where you bind your data(variables) and code(methods) together as a single unit. Here, the data is hidden from the outer world and can be accessed only via current class methods. This helps in protecting the data from any unnecessary modification. We can achieve encapsulation in Java by:
- Declaring the variables of a class as private.
- Providing public setter and getter methods to modify and view the values of the variables.
Q12. What is an association?
Association is a relationship where all object have their own lifecycle and there is no owner. Let’s take the example of Teacher and Student. Multiple students can associate with a single teacher and a single student can associate with multiple teachers but there is no ownership between the objects and both have their own lifecycle. These relationships can be one to one, one to many, many to one and many to many.
Q13. What do you mean by aggregation?
An aggregation is a specialized form of Association where all object has their own lifecycle but there is ownership and child object can not belong to another parent object. Let’s take an example of Department and teacher. A single teacher can not belong to multiple departments, but if we delete the department teacher object will not destroy.
Q14. What is composition in Java?
Composition is again a specialized form of Aggregation and we can call this as a “death” relationship. It is a strong type of Aggregation. Child object does not have their lifecycle and if parent object deletes all child object will also be deleted. Let’s take again an example of a relationship between House and rooms. House can contain multiple rooms there is no independent life of room and any room can not belongs to two different houses if we delete the house room will automatically delete.
Q15. What is a marker interface?
A Marker interface can be defined as the interface having no data member and member functions. In simpler terms, an empty interface is called the Marker interface. The most common examples of Marker interface in Java are Serializable, Cloneable etc. The marker interface can be declared as follows.
|
1
2
|
public interface Serializable{} |
Q16. What is object cloning in Java?
Object cloning in Java is the process of creating an exact copy of an object. It basically means the ability to create an object with a similar state as the original object. To achieve this, Java provides a method clone() to make use of this functionality. This method creates a new instance of the class of the current object and then initializes all its fields with the exact same contents of corresponding fields. To object clone(), the marker interface java.lang.Cloneable must be implemented to avoid any runtime exceptions. One thing you must note is Object clone() is a protected method, thus you need to override it.
Q17. What is a copy constructor in Java?
Copy constructor is a member function that is used to initialize an object using another object of the same class. Though there is no need for copy constructor in Java since all objects are passed by reference. Moreover, Java does not even support automatic pass-by-value.
Q18. What is a constructor overloading in Java?
In Java, constructor overloading is a technique of adding any number of constructors to a class each having a different parameter list. The compiler uses the number of parameters and their types in the list to differentiate the overloaded constructors.
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
|
class Demo{int i;public Demo(int a){i=k;}public Demo(int a, int b){//body} |
Servlets Interview Questions
Q1. What is a servlet?
- Java Servlet is server-side technologies to extend the capability of web servers by providing support for dynamic response and data persistence.
- The javax.servlet and javax.servlet.http packages provide interfaces and classes for writing our own servlets.
- All servlets must implement the javax.servlet.Servlet interface, which defines servlet lifecycle methods. When implementing a generic service, we can extend the GenericServlet class provided with the Java Servlet API. The HttpServlet class provides methods, such as doGet() and doPost(), for handling HTTP-specific services.
- Most of the times, web applications are accessed using HTTP protocol and thats why we mostly extend HttpServlet class. Servlet API hierarchy is shown in below image.

Q2. What are the differences between Get and Post methods?
| Get | Post |
|---|---|
| Limited amount of data can be sent because data is sent in header. | Large amount of data can be sent because data is sent in body. |
| Not Secured because data is exposed in URL bar. | Secured because data is not exposed in URL bar. |
| Can be bookmarked | Cannot be bookmarked |
| Idempotent | Non-Idempotent |
| It is more efficient and used than Post | It is less efficient and used |
Q3. What is Request Dispatcher?
RequestDispatcher interface is used to forward the request to another resource that can be HTML, JSP or another servlet in same application. We can also use this to include the content of another resource to the response.
There are two methods defined in this interface:
1.void forward()
2.void include()
Q4. What are the differences between forward() method and sendRedirect() methods?
| forward() method | SendRedirect() method |
|---|---|
| forward() sends the same request to another resource. | sendRedirect() method sends new request always because it uses the URL bar of the browser. |
| forward() method works at server side. | sendRedirect() method works at client side. |
| forward() method works within the server only. | sendRedirect() method works within and outside the server. |
Q5. What is the life-cycle of a servlet?
There are 5 stages in the lifecycle of a servlet:
- Servlet is loaded
- Servlet is instantiated
- Servlet is initialized
- Service the request
- Servlet is destroyed
Q6. How does cookies work in Servlets?
- Cookies are text data sent by server to the client and it gets saved at the client local machine.
- Servlet API provides cookies support through javax.servlet.http.Cookie class that implements Serializable and Cloneable interfaces.
- HttpServletRequest getCookies() method is provided to get the array of Cookies from request since there is no point of adding Cookie to request, there are no methods to set or add a cookie to request.
- Similarly, HttpServletResponse addCookie(Cookie c) method is provided to attach cookie in the response header, there are no getter methods for a cookie.
Q7. What are the differences between ServletContext vs ServletConfig?
The difference between ServletContext and ServletConfig in Servlets JSP is in below tabular format.
| ServletConfig | ServletContext |
|---|---|
| Servlet config object represent single servlet | It represent whole web application running on particular JVM and common for all the servlet |
| Its like local parameter associated with particular servlet | Its like global parameter associated with whole application |
| It’s a name value pair defined inside the servlet section of web.xml file so it has servlet wide scope | ServletContext has application wide scope so define outside of servlet tag in web.xml file. |
| getServletConfig() method is used to get the config object | getServletContext() method is used to get the context object. |
| for example shopping cart of a user is a specific to particular user so here we can use servlet config | To get the MIME type of a file or application session related information is stored using servlet context object. |
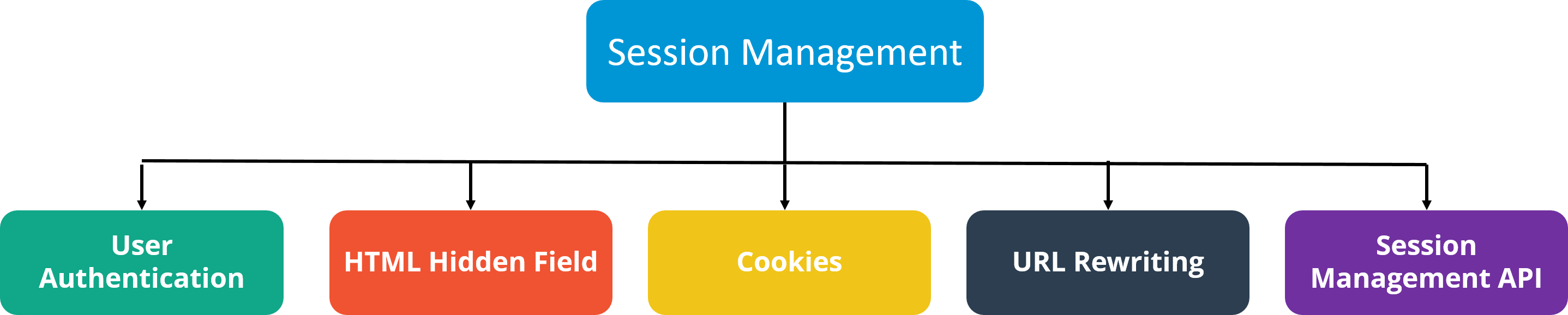
Q8. What are the different methods of session management in servlets?
Session is a conversational state between client and server and it can consists of multiple request and response between client and server. Since HTTP and Web Server both are stateless, the only way to maintain a session is when some unique information about the session (session id) is passed between server and client in every request and response.
Some of the common ways of session management in servlets are:
- User Authentication
- HTML Hidden Field
- Cookies
- URL Rewriting
- Session Management API
JDBC Interview Questions
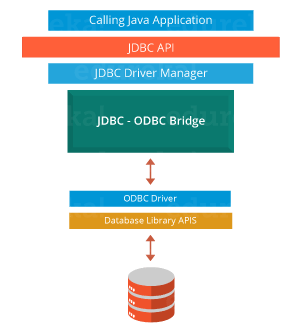
1. What is JDBC Driver?
JDBC Driver is a software component that enables java application to interact with the database. There are 4 types of JDBC drivers:
- JDBC-ODBC bridge driver
- Native-API driver (partially java driver)
- Network Protocol driver (fully java driver)
- Thin driver (fully java driver)
2. What are the steps to connect to a database in java?
- Registering the driver class
- Creating connection
- Creating statement
- Executing queries
- Closing connection
3. What are the JDBC API components?
The java.sql package contains interfaces and classes for JDBC API.
Interfaces:
- Connection
- Statement
- PreparedStatement
- ResultSet
- ResultSetMetaData
- DatabaseMetaData
- CallableStatement etc.
Classes:
- DriverManager
- Blob
- Clob
- Types
- SQLException etc.
4. What is the role of JDBC DriverManager class?
The DriverManager class manages the registered drivers. It can be used to register and unregister drivers. It provides factory method that returns the instance of Connection.
5. What is JDBC Connection interface?
The Connection interface maintains a session with the database. It can be used for transaction management. It provides factory methods that returns the instance of Statement, PreparedStatement, CallableStatement and DatabaseMetaData.
6. What is the purpose of JDBC ResultSet interface?
The ResultSet object represents a row of a table. It can be used to change the cursor pointer and get the information from the database.
7. What is JDBC ResultSetMetaData interface?
The ResultSetMetaData interface returns the information of table such as total number of columns, column name, column type etc.
8. What is JDBC DatabaseMetaData interface?
The DatabaseMetaData interface returns the information of the database such as username, driver name, driver version, number of tables, number of views etc.
9. What do you mean by batch processing in JDBC?
Batch processing helps you to group related SQL statements into a batch and execute them instead of executing a single query. By using batch processing technique in JDBC, you can execute multiple queries which makes the performance faster.
10. What is the difference between execute, executeQuery, executeUpdate?
Statement execute(String query) is used to execute any SQL query and it returns TRUE if the result is an ResultSet such as running Select queries. The output is FALSE when there is no ResultSet object such as running Insert or Update queries. We can use getResultSet() to get the ResultSet and getUpdateCount() method to retrieve the update count.
Statement executeQuery(String query) is used to execute Select queries and returns the ResultSet. ResultSet returned is never null even if there are no records matching the query. When executing select queries we should use executeQuery method so that if someone tries to execute insert/update statement it will throw java.sql.SQLException with message “executeQuery method can not be used for update”.
Statement executeUpdate(String query) is used to execute Insert/Update/Delete (DML) statements or DDL statements that returns nothing. The output is int and equals to the row count for SQL Data Manipulation Language (DML) statements. For DDL statements, the output is 0.
You should use execute() method only when you are not sure about the type of statement else use executeQuery or executeUpdate method.
Q11. What do you understand by JDBC Statements?
JDBC statements are basically the statements which are used to send SQL commands to the database and retrieve data back from the database. Various methods like execute(), executeUpdate(), executeQuery, etc. are provided by JDBC to interact with the database.
JDBC supports 3 types of statements:
- Statement: Used for general purpose access to the database and executes a static SQL query at runtime.
- PreparedStatement: Used to provide input parameters to the query during execution.
- CallableStatement: Used to access the database stored procedures and helps in accepting runtime parameters.
Spring Interview Questions
Q1. What is Spring?
Wikipedia defines the Spring framework as “an application framework and inversion of control container for the Java platform. The framework’s core features can be used by any Java application, but there are extensions for building web applications on top of the Java EE platform.” Spring is essentially a lightweight, integrated framework that can be used for developing enterprise applications in java.
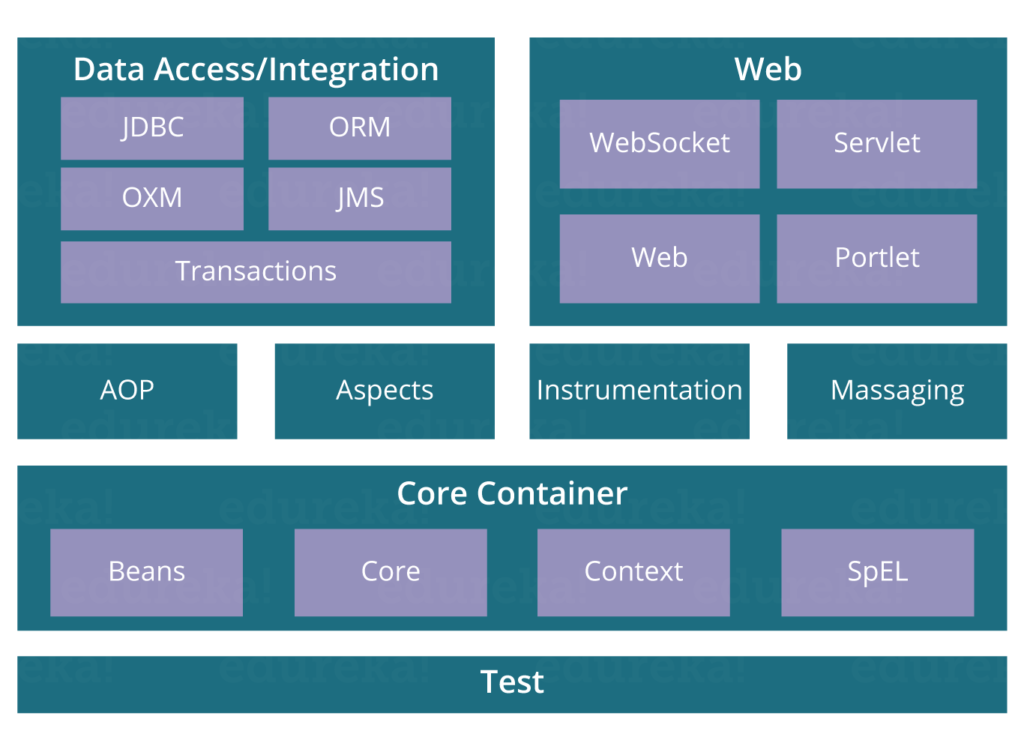
Q2. Name the different modules of the Spring framework.
Some of the important Spring Framework modules are:
- Spring Context – for dependency injection.
- Spring AOP – for aspect oriented programming.
- Spring DAO – for database operations using DAO pattern
- Spring JDBC – for JDBC and DataSource support.
- Spring ORM – for ORM tools support such as Hibernate
- Spring Web Module – for creating web applications.
- Spring MVC – Model-View-Controller implementation for creating web applications, web services etc.
Q3. List some of the important annotations in annotation-based Spring configuration.
The important annotations are:
- @Required
- @Autowired
- @Qualifier
- @Resource
- @PostConstruct
- @PreDestroy
Q4. Explain Bean in Spring and List the different Scopes of Spring bean.
Beans are objects that form the backbone of a Spring application. They are managed by the Spring IoC container. In other words, a bean is an object that is instantiated, assembled, and managed by a Spring IoC container.
There are five Scopes defined in Spring beans.

- Singleton: Only one instance of the bean will be created for each container. This is the default scope for the spring beans. While using this scope, make sure spring bean doesn’t have shared instance variables otherwise it might lead to data inconsistency issues because it’s not thread-safe.
- Prototype: A new instance will be created every time the bean is requested.
- Request: This is same as prototype scope, however it’s meant to be used for web applications. A new instance of the bean will be created for each HTTP request.
- Session: A new bean will be created for each HTTP session by the container.
- Global-session: This is used to create global session beans for Portlet applications.
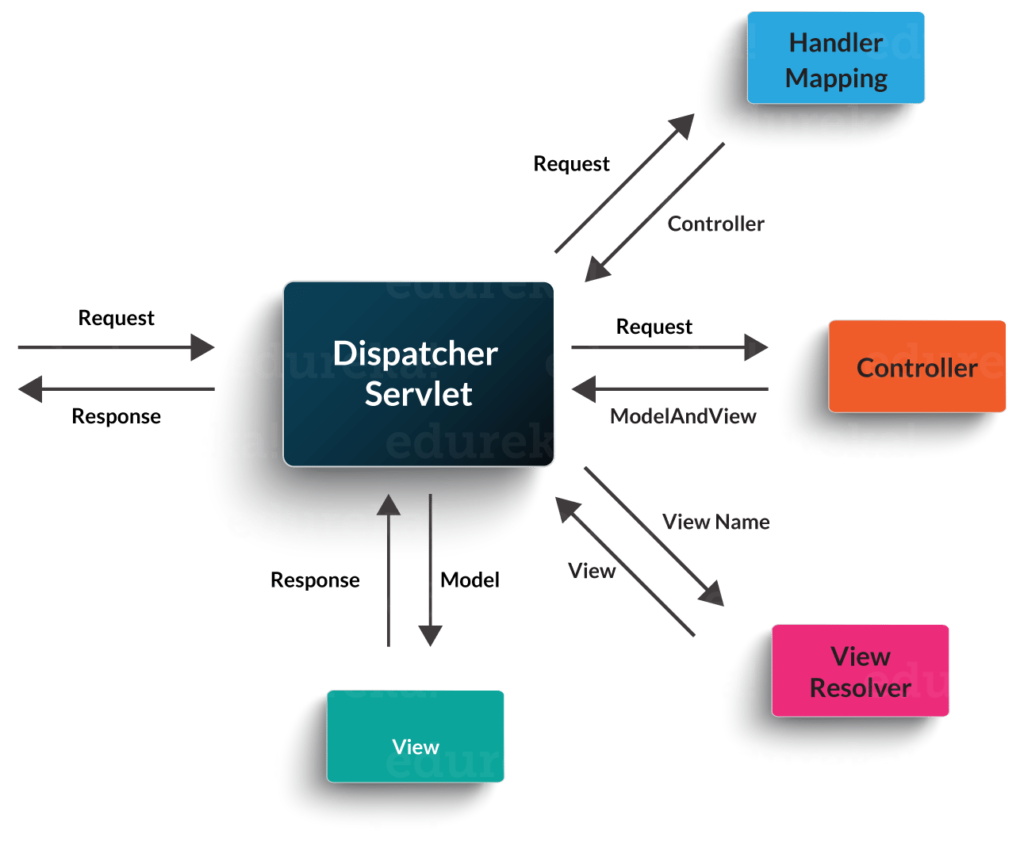
Q5. Explain the role of DispatcherServlet and ContextLoaderListener.
DispatcherServlet is basically the front controller in the Spring MVC application as it loads the spring bean configuration file and initializes all the beans that have been configured. If annotations are enabled, it also scans the packages to configure any bean annotated with @Component, @Controller, @Repository or @Service annotations.
ContextLoaderListener, on the other hand, is the listener to start up and shut down the WebApplicationContext in Spring root. Some of its important functions includes tying up the lifecycle of Application Context to the lifecycle of the ServletContext and automating the creation of ApplicationContext.
Q6. What are the differences between constructor injection and setter injection?
| No. | Constructor Injection | Setter Injection |
| 1) | No Partial Injection | Partial Injection |
| 2) | Doesn’t override the setter property | Overrides the constructor property if both are defined. |
| 3) | Creates a new instance if any modification occurs | Doesn’t create a new instance if you change the property value |
| 4) | Better for too many properties | Better for a few properties. |
Q7. What is autowiring in Spring? What are the autowiring modes?
Autowiring enables the programmer to inject the bean automatically. We don’t need to write explicit injection logic. Let’s see the code to inject bean using dependency injection.