A user equipmentʼs initial access in NR is per- formed according to a procedure that involves the steps of detecting a Synchronization Signal (SS), acquiring broadcast system information, and es-tablishing connection with the network by a ran- dom access procedure.
3.1 SS/PBCH Block
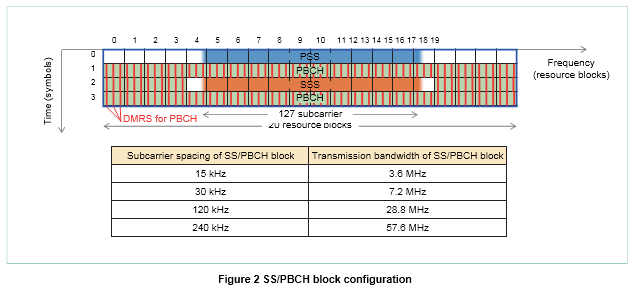
As in LTE, the SS in NR consists of two signals: a Primary Synchronization Signal (PSS), and a Secondary Synchronization Signal (SSS). The SS together with the PBCH and the DeModulation Reference Signals for PBCH (DMRS for PBCH) forms an SS/PBCH block as shown in Figure 2.The base station uses this SS/PBCH block to provide information that is essential for initial access and mobility, including system parameters whereby user equipment can discover NR cells, establish frame synchronization, measure the downlink re- ception quality, and carry out other actions neces- sary for the reception of system information. The base station can set the transmission timing and transmission period of the SS/PBCH block for each carrier, and indicates this information to the user equipment.
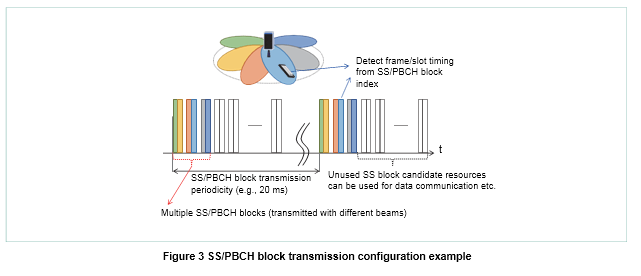
In NR, multiple resources for SS/PBCH block transmission are defined within a half frame of 5 ms duration, where the maximum number of SS/ PBCH block transmissions per carrier depends on the frequency band. As shown in Figure 3, the num- ber of SS/PBCH blocks to be transmitted can be set according to factors such as the base station
antenna configuration. With multiple SS/PBCH blocks, different beamforming can be applied to each SS/ PBCH block in order to increase the communica-tion range and expand the area of coverage.
3.2 System Information Notification
Broadcast information in NR can be classified into three types: broadcast information transmitted by the PBCH, system information necessary for ini- tial access, and other system information. The PBCH includes a System Frame Number (SFN) and information that user equipment needs to establish frame synchronization with a NR cell after detecting an SS/PBCH block, such as an index for identifying the symbol position of the detected SS/PBCH block in a half frame. The PBCH also carries system parameters that are needed for the reception of System Information Block type 1 (SIB 1), which is described below. To perform random access, it is necessary to have information such as the uplink carrier infor- mation and random access signal configuration in- formation. This is included as part of the information necessary for initial access, which is broadcast to the user equipment in an NR cell as SIB1.
3.3 Random Access
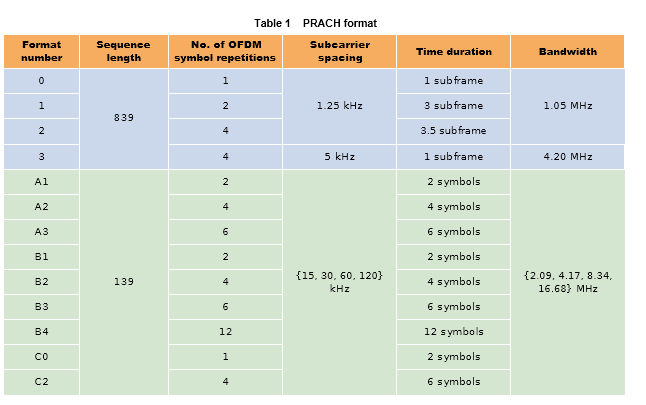
Random access in NR is performed in four steps in the same way as in LTE. At the first step, the user equipment transmits a Physical Random Access CHannel (PRACH) to the base station. As shown in Table 1, NR defines 13 PRACH formats in total, including some formats with fixed subcarrier spacings that follow the de- sign of LTE PRACH, and other formats with vari- able subcarrier spacings that can fit into the dura- tion of an integer number of symbols in an NR slot. When a base station is operated with beamform- ing, where different beams are applied to multiple SS/PBCH block transmissions, different PRACH transmission resources are associated with differ- ent SS/PBCH blocks. The user equipment transmits a PRACH to initiate random access by using the PRACH resource associated with the selected
SS/PBCH block. In this way, the base station can use the received PRACH resources to figure out which SS/PBCH block (and thus which beamform- ing direction) was received by the user equipment transmitting a PRACH. Therefore, in the subse- quent random access procedure consisting of ran- dom access response reception, connection request message transmission and contention resolution mes- sage reception, the base station can use transmis- sion/reception beamforming directed specifically to the user equipment.
3.4 Mobility
In NR, as in LTE, the base station performs tasks such as selecting serving cells, performing hando- vers and adding/deleting secondary cells based on the report from corresponding user equipment re- garding measurement results on downlink reference signals. The SSS included in the SS/PBCH block transmitted by the base station is a basic cell-specific reference signal in NR. The user equipment uses it to measure and report the Reference Signal Re- ceived Power (RSRP) and Reference Signal Received Quality (RSRQ) in each cell according to settings from the base station.